VD/VOD TREATMENT
- General information
- Variations
- Our design – your advantage
- Digitalization
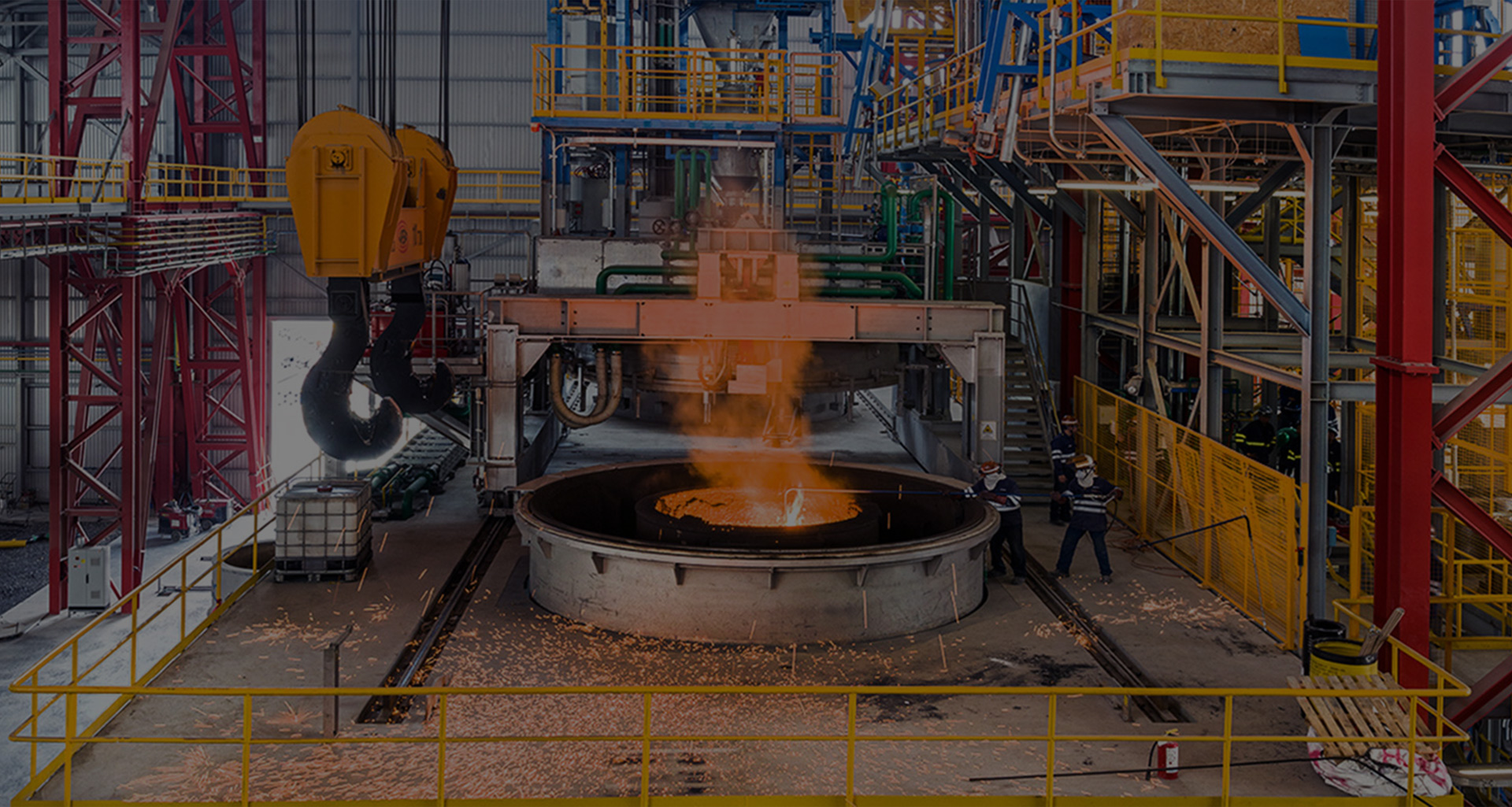
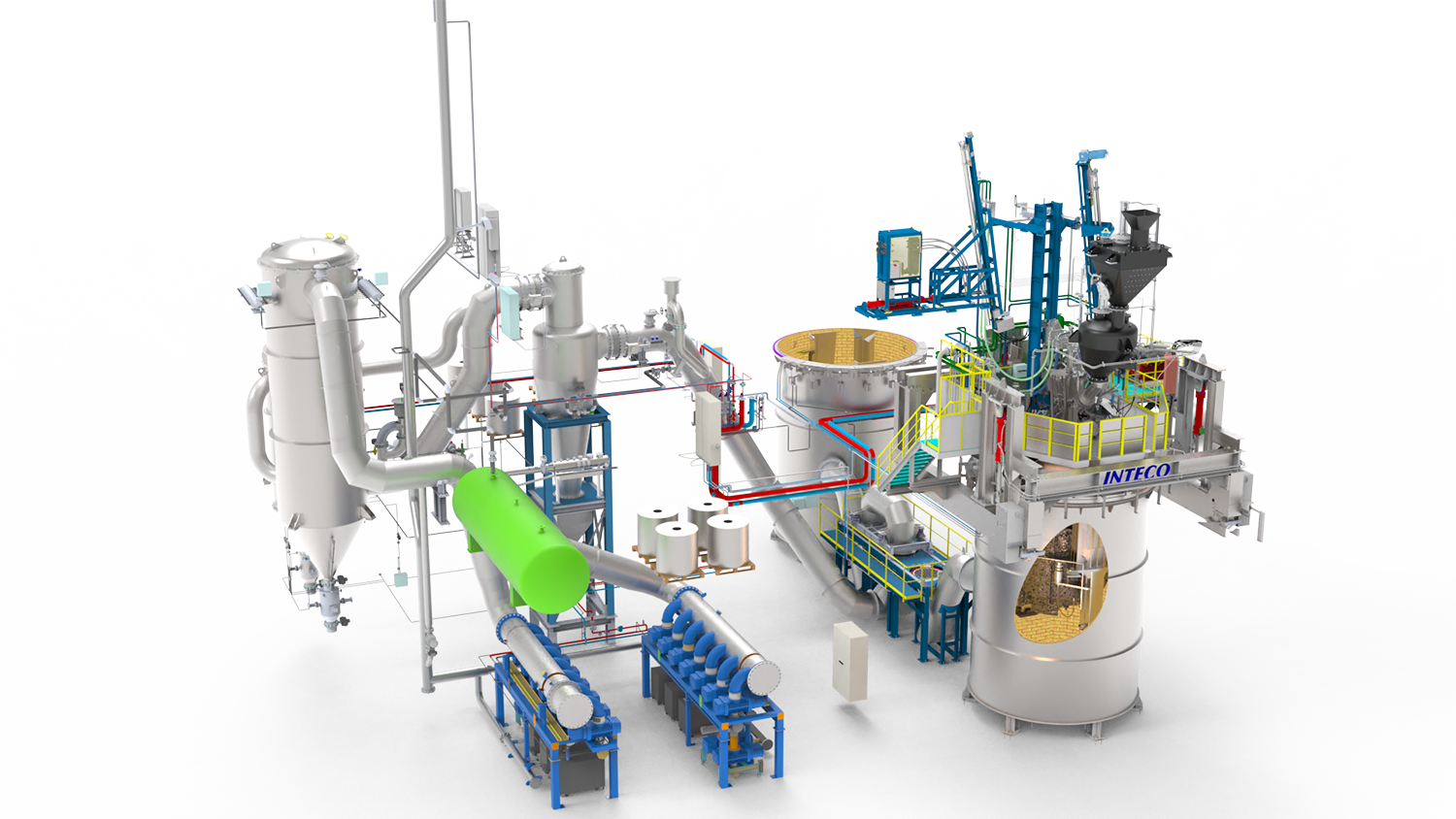
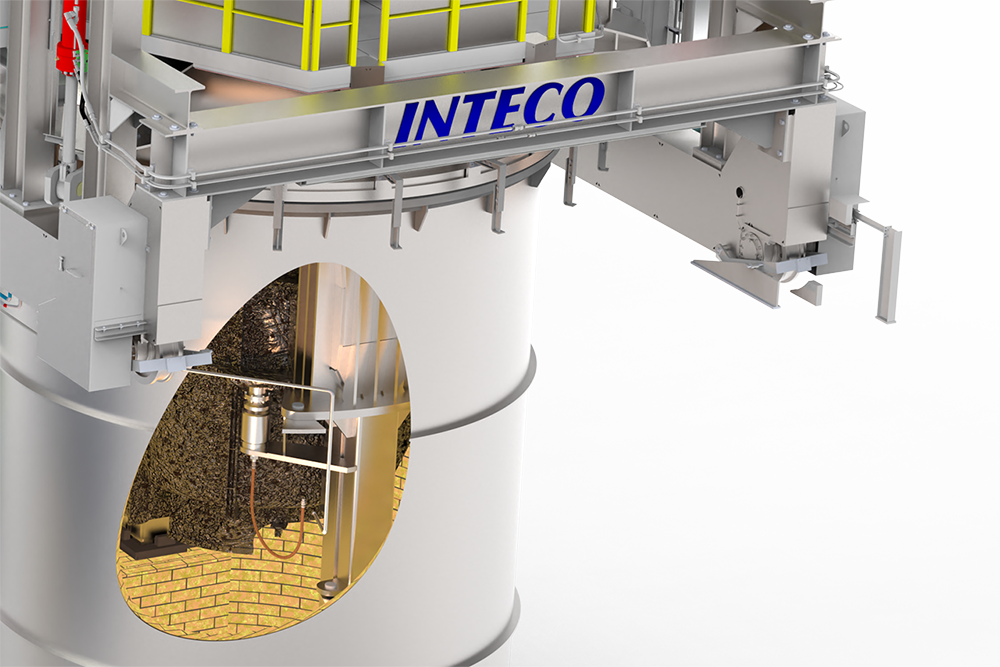
The vacuum treatment (VD) is one of the most commonly used commercial degassing process. Therefore a ladle is placed inside a vacuum tank and closed with a vacuum cover for operation under vacuum conditions. The ladle is equipped with a porous plug for inert gas stirring. Vacuum is created by steam ejector system or by dry mechanical vacuum pumps. The main purpose of the vacuum treatment is to reduce to the required limit values, carbon, oxygen, nitrogen and hydrogen. The VD system can also be equipped with vacuum alloy hoppers so that an analysis correction and final adjustments can be made. Further advantages of the process are excellent homogenization and high alloy yields. During VOD treatment very low carbon contents and high chromium yield can be achieved by oxygen blowing under vacuum operation. Most production programs nowadays require a combination of VD and VOD operation. For that purpose, the equipment can be designed for both types of operations.
Overall, VD/VOD treatment offers the following process advantages:
- Utilisation of cheaper materials with high carbon content
- Reduction of production costs
- Improvement of quality thanks to low gas content
- Ability to produce ELC qualities with minimum chromium loss
- Achievability of strict analysis tolerances
- High chromium yield
- Tank degassers: Single or twin operation stand
- Heat sizes up to 350t
- Ladle degassing unit: DETEM for small heat sizes
- Steam ejector vacuum pumps and dry mechanical vacuum pumps
- Alloying under vacuum conditions
The right auxiliary equipment is crucial for efficient, high-quality and safe production. Precise temperature measurements, automatic sampling and robust and high-temperature resistant components such as the gas coupler not only increase quality, but also improve operator safety. In addition, INTECO’s “zero-leakage” design helps to keep pump down and treatment times short and thus reduces operating costs. Sophisticated concepts for vacuum tank transfer cars and ladle covers complete the package.

A unique feature of the INTECO VD/VOD system is the consistent “zero-leakage design”. All operations, such as wire feeding, temperature measurement and sampling, are carried out through the central socket. As only one single opening is required in the vacuum cover, there is less risk of leakage. This results in very short pump-down and treatment times and low operating costs.
Digitalisierung und Smart Production sind die treibenden Kräfte für Entwicklung und Veränderung in der Stahlbranche. Bei INTECO bieten wir Ihnen nicht nur erstklassiges Engineering im Anlagenbau, sondern auch maßgeschneiderte digitale Lösungen, die den anspruchsvollen Anforderungen unserer Kunden gerecht werden. Überwachen Sie Ihre Produktion effizienter und nutzen Sie die gesammelten Informationen für Anpassungen und Fortschritt.
The oxygen model calculates the required amount of oxygen to achieve target decarburization, considering initial steel samples and current temperature that lead to a physically based oxygen quantity. It uses the basics of the thermochemical and thermodynamic approach and once the vacuum and/or oxygen blowing has started, the decarburization model tracks the oxidation of the elements involved. The chemical composition is updated through close interaction with the thermochemical model. The decarburization model reacts to the oxygen injection rate and oxidizes the steel according to the thermodynamic evaluations. The decarburization model constantly checks stoichiometric oxidation against kinetic reactions and the temperature gain is back-looped to the temperature model. The degassing model calculates the removal of hydrogen and nitrogen.
INTECO’s Material Handling System Automation offers precise and time-critical alloying for all secondary metallurgy plants. Its recipe-based approach serves various technologies such as positive and negative weighing, shuttles, weighing bands, or hoppers and integrates micro-dosing systems and wire feeding machines. Moreover, it provides fallback modes for redundant feeding lines as well as sequential dosing of materials or material groups to add slag builders and alloys in the correct order.
The smart process camera is a retractable and therefore well protected optical system that directly streams a high-resolution video to the control room to ensure safe low-manpower operation. The optional thermal imaging variant provides a clear view through smoke and dust and serves for automatic stirring adjustment. Additional generated process information such as slag height and stirring eye detection enhances metallurgical model accuracy and safety.
The thermochemical model calculates oxide and element activities based on current process conditions and events, current heat state and energy losses and gains. In this context, IMAS modeling includes a thermophysical property library, reaction enthalpies, coefficients for interactions providing the necessary parameters, and coefficients to determine and calculate the activities.
The temperature model accounts for the temperature losses due to radiation and convection as well as the changes in temperature due to purging, material addition and heating. Temperature changes due to reactions are also taken into account and are therefore coupled with the basic thermochemical model. Both are not only used to calculate the actual heat state but also to predict take-over time and temperature.
The degassing model calculates the reduction of hydrogen and nitrogen in the VD system.
The IPAS off-gas measuring system/device for VOD applications includes a gas extraction system, an off-gas analyzer and a flow measurement device. The off-gas analyzer measures CO and CO2 using an infrared photometer, H2 using thermal conductivity and O2 using electromagnetic force measurement. The flow meter works based on ultrasound measurements or hot-wire anemometer and is supplied with temperature and pressure data for normalization to standard cubic meters per hour. The IPAS system is self-calibrating and works with online process models for hybrid decarburization and degassing modelling.
IMAS-PA-VD/VOD provides advanced top-down process guidance through dynamic or static treatment planning and integrated optimization tools. Process supervision is massively improved by the cockpit view and integrated real-time process models. IMAS provides instant real-time information and alerts, based on which the operators can control and steer the process just-in-time. The heat-based data recording stores sensor data, including complex information such as video streams, allowing observation of real-time data for quality assurance and process improvement.
PROJECTS

Nucor Darlington
Type: 110t VD
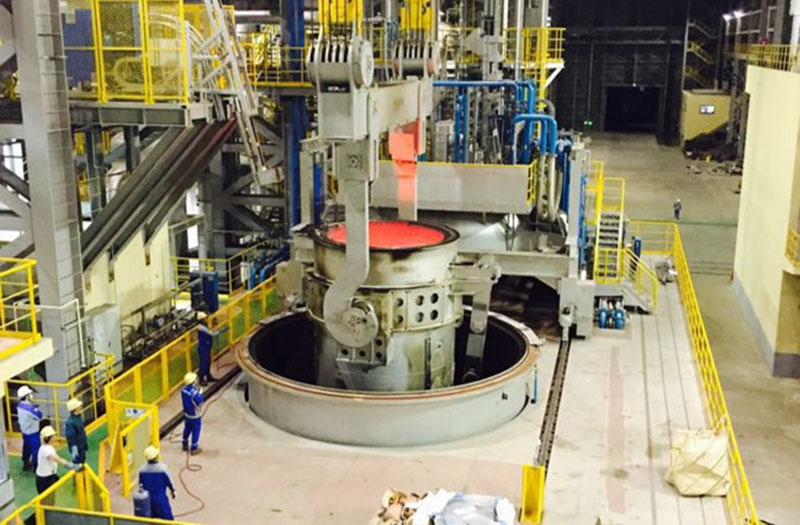

Taewoong Special Steel
Type: 150t VD/VOD
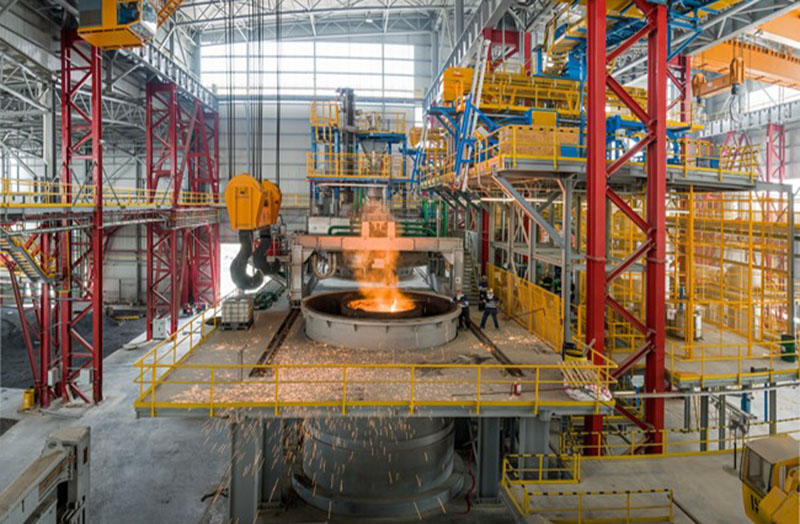

Grupo FRISA
Type: 50t VD
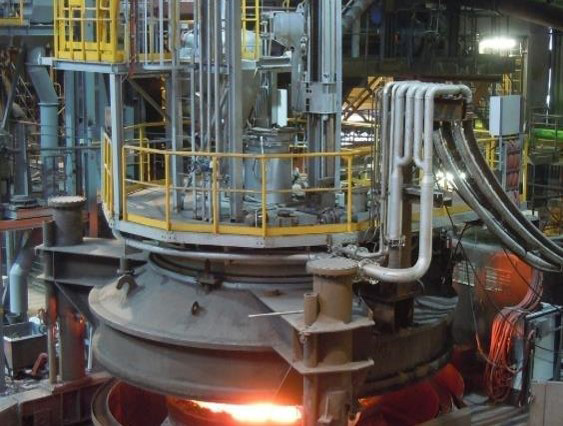

Deutsche Edelstahlwerke Specialty Steel
Type: 130t VD/VOD
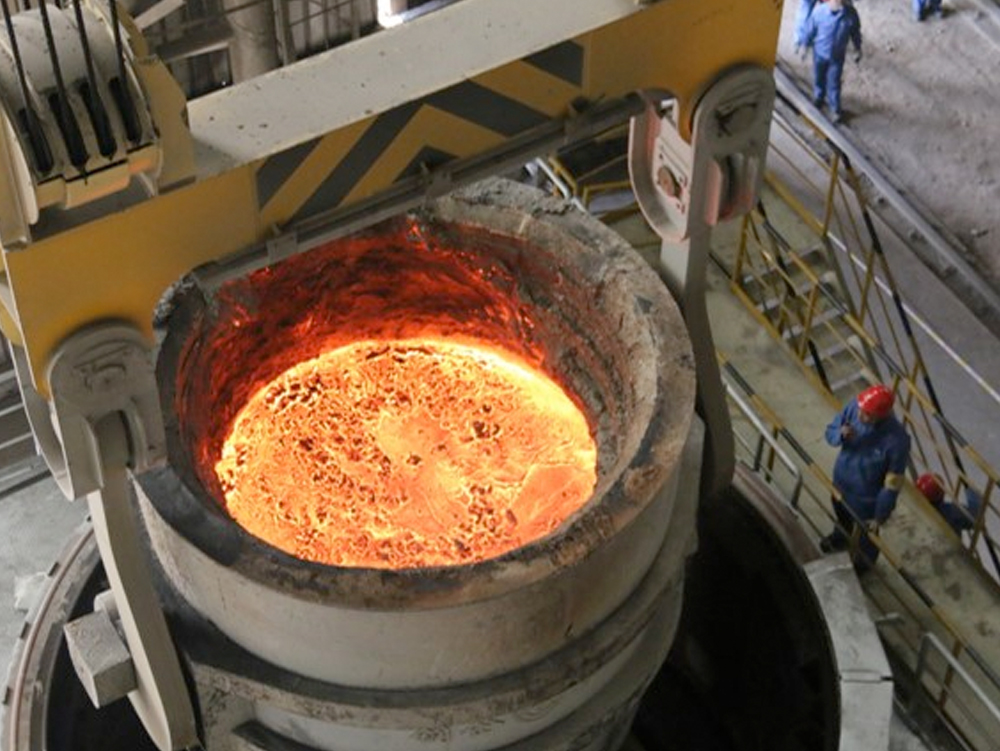

Taigang Stainless Steel
Type: 45t VD/VOD
Nucor Darlington
Type: 110t VD
Taewoong Special Steel
Type: 150t VD/VOD
Grupo FRISA
Type: 50t VD
Deutsche Edelstahlwerke
Specialty Steel
Type: 130t VD/VOD
Taigang Stainless Steel
Type: 45t VD/VOD